986. Interval List Intersections
Problem
You are given two lists of closed intervals, firstList and secondList, where firstList[i] = [starti, endi] and secondList[j] = [startj, endj]. Each list of intervals is pairwise disjoint and in sorted order.
Return the intersection of these two interval lists.
A closed interval [a, b] (with a < b) denotes the set of real numbers x with a <= x <= b.
The intersection of two closed intervals is a set of real numbers that are either empty or represented as a closed interval. For example, the intersection of [1, 3] and [2, 4] is [2, 3].
Example 1:
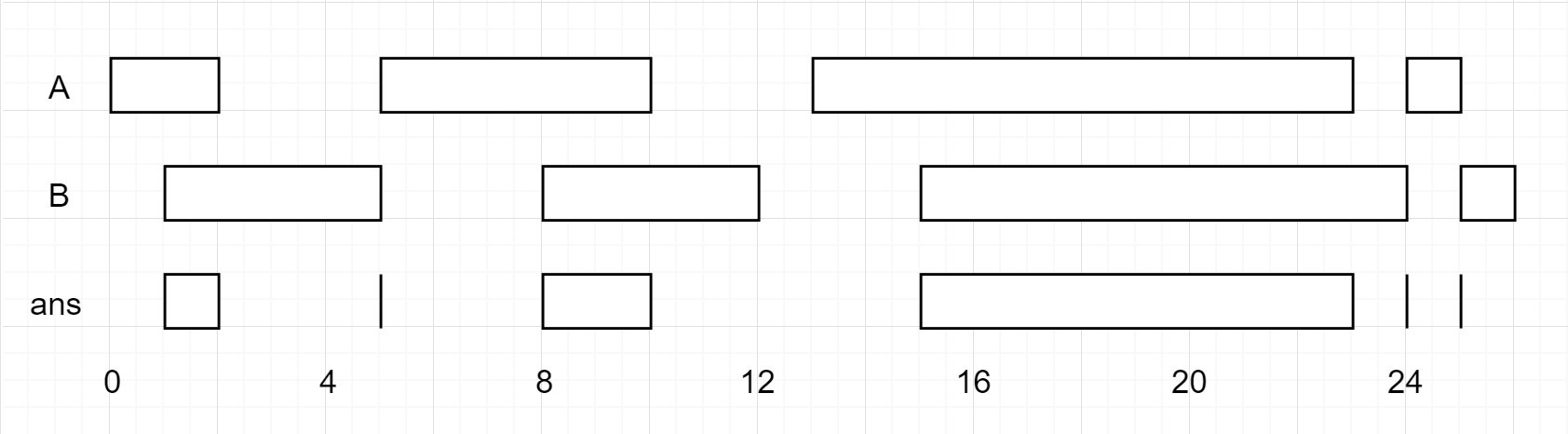
Input: firstList = [[0,2],[5,10],[13,23],[24,25]], secondList = [[1,5],[8,12],[15,24],[25,26]] Output: [[1,2],[5,5],[8,10],[15,23],[24,24],[25,25]]
Example 2:
Input: firstList = [[1,3],[5,9]], secondList = [] Output: []
Example 3:
Input: firstList = [], secondList = [[4,8],[10,12]] Output: []
Example 4:
Input: firstList = [[1,7]], secondList = [[3,10]] Output: [[3,7]]
Constraints:
0 <= firstList.length, secondList.length <= 1000firstList.length + secondList.length >= 10 <= starti < endi <= 109endi < starti+10 <= startj < endj <= 109endj < startj+1
Discussion
This problem requires us to find intersection between two list of intervals.
Given that each list of intervals is pairwise disjoint and sorted, we do not have to handle the complicated case within each list.
We imagine this problem can be solved with a two-pointer approach. We set up two individual pointers on each list and moving along the list. In each iteration we only compare one interval from each list.
We keep updating the pointer in the list with a smaller interval and eventually every pairs of interval with chance of intersecting will be evaluated.
Now the problem looks to have a linear solution, all left to be done is the pair evaluation. Below we can list out 6 scenarios for possible interval.
| Interval A | Interval B | Intersection | Interval to be Updated |
|---|---|---|---|
| [1, 2] | [2, 3] | [2, 2] | A |
| [3, 4] | [2, 3] | [3, 3] | B |
| [3, 4] | [5, 6] | [] | A |
| [7, 8] | [5, 6] | [] | B |
| [3, 4] | [2, 5] | [3, 4] | A |
| [1, 6] | [4, 5] | [4, 5] | B |
Based on the listed out scenarios, we can observe two action to be taken in the evaluation step:
- Intersection of two interval is
[max(low_a, low_b), min(high_a, high_b)], if exists. - The interval lower upper limit is to be updated.
Based on this we can implement our solution.
Solution
The code implementation is simple.
After some empty case checking we initialize two pointers, and the evaluation is done in a single while loop.
class Solution:
def intervalIntersection(
self,
firstList: List[List[int]],
secondList: List[List[int]]
) -> List[List[int]]:
if len(firstList) == 0 or len(secondList) == 0:
return []
i, j, result = 0, 0, []
while i < len(firstList) and j < len(secondList):
low = max(firstList[i][0], secondList[j][0])
high = min(firstList[i][1], secondList[j][1])
if low <= high:
result.append([low, high])
if firstList[i][1] < secondList[j][1]:
i += 1
else:
j += 1
return resultComplexity Analysis
- Time Complexity:
O(m + n), as only a single loop with two pointers in two lists. - Space Complexity:
O(n), as the answer for this problem is a list with size limited by input,n.